What Does the Brain Do?
Some common facts about your brain, the mind controls what you think and feel, how you learn and recollect, and how you move and talk. Yet, it additionally controls things you’re less mindful of — like the pulsating of your heart and the absorption of your food.
Think about the cerebrum as a focal PC that controls all the body’s capacities. The remainder of the sensory system resembles an organization that transfers messages to and fro from the cerebrum to various pieces of the body. It does this utilizing the spinal string, which runs starting from the brain through the back. It contains threadlike nerves that branch out to each organ and body part.
At the point when a message comes into the mind from anyplace in the body, the cerebrum advises the body how to respond. For instance, on the off chance that you contact a hot oven, the nerves in your skin shoot a message of agony to your cerebrum. The mind at that point communicates something specific back advising the muscles in your grasp to pull away. Fortunately, this neurological handoff race occurs in a moment.
What Are the Parts of the Nervous System?
The sensory system is comprised of the focal sensory system and the fringe sensory system:
The cerebrum and the spinal line are the focal sensory system.
The nerves that experience the entire body make up the fringe sensory system.
The human cerebrum is inconceivably minimal, weighing only 3 pounds. It has numerous folds and scores, however. These give it the additional surface zone required for putting away the body’s significant data.
The spinal rope is a long heap of nerve tissue around 18 inches in length and 1/2-inch thick. It reaches out from the lower part of the mind down through the spine. En route, nerves branch out to the whole body.
The mind and the spinal string are secured by bone: the cerebrum by the bones of the skull, and the spinal line by a lot of ring-molded bones called vertebrae. They’re both padded by layers of films called meninges and an exceptional liquid called cerebrospinal liquid. This liquid secures the nerve tissue, keep it sound, and eliminate squander items.
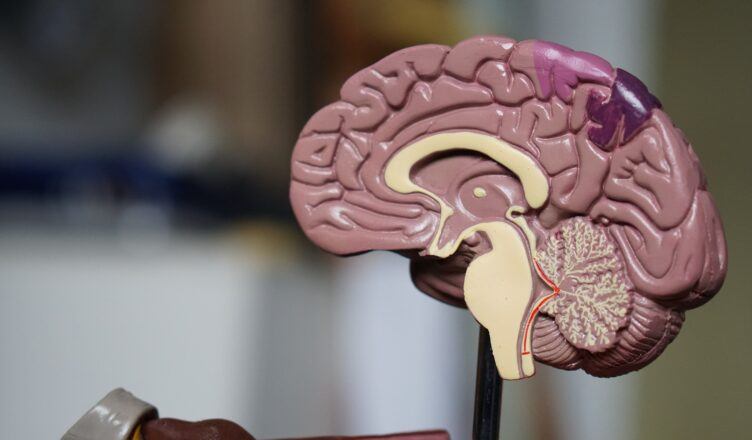
What Are the Parts of the Brain?
The cerebrum has three principal areas: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain.
The Forebrain
The forebrain is the biggest and most complex aspect of the cerebrum. It comprises of the cerebrum — the zone with all the folds and furrows regularly found in photos of the mind — just as different structures under it.
The cerebrum contains the data that makes you what your identity is: your insight, memory, character, feeling, discourse, and capacity to feel and move. Explicit regions of the cerebrum are accountable for preparing these various kinds of data. These are called flaps, and there are four of them: the frontal, parietal, fleeting, and occipital projections.
The cerebrum has both ways parts, called halves of the globe. They’re associated in the center by a band of nerve strands (the corpus callosum) that allows them to convey. These parts may seem as though identical representations of one another, however, numerous researchers accept they have various capacities:
So when you’re adjusting your checkbook, you’re utilizing the left side. At the point when you’re tuning in to music, you’re utilizing the correct side. It’s accepted that a few people are more “right-brained” or “left-brained” while others are more “entire brained,” which means they utilize the two parts of their cerebrum similarly.
The external layer of the cerebrum is known as the cortex (otherwise called “dim issue”). Data gathered by the five detects comes into the cerebrum to the cortex.
In the internal aspect of the forebrain sits the thalamus, nerve center, and pituitary organ :
The thalamus conveys messages from the tangible organs like the eyes, ears, nose, and fingers to the cortex.
The nerve center likewise controls the pituitary organ, which makes the hormones that control development, Some common facts about your brain, digestion, water, and mineral equalization, sexual development, and reaction to stretch.
The Midbrain – Some common facts about your brain
The hindbrain sits underneath the back finish of the cerebrum. It comprises of the cerebellum, pons, and medulla. The cerebellum — additionally called the “little mind” since it would appear that a little form of the cerebrum — is liable for equalization, development, and coordination.
TThe brainstem takes in, conveys, and arranges the cerebrum’s messages. It additionally controls a large number of the body’s programmed capacities, such as breathing, pulse, circulatory strain, gulping, assimilation, and blinking. How Does the Nervous System Work?
The essential operations of the sensory system rely a ton upon minuscule cells called neurons. The cerebrum has billions of them, and they have many particular positions. For instance, tactile neurons send data from the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin to the mind. Engine neurons divert messages from the cerebrum to the remainder of the body.
Insight, learning, and memory. As you develop and learn, messages make a trip starting with one neuron then onto the next again and again, making associations, or pathways, in the mind.
Some common facts about your brain
In little youngsters, the cerebrum is exceptionally versatile. . Yet, as you age, the mind needs to work more diligently to make new neural pathways, making it harder to ace new assignments or changeset personal conduct standards. That is the reason numerous researchers trust it’s imperative to continue provoking the mind to learn new things and make new associations — it helps keeps the cerebrum dynamic throughout a lifetime.
Memory is another unpredictable capacity of the cerebrum. The things you’ve done, learned, and seen are first handled in the cortex. At that point, if you sense that this data is sufficiently significant to recollect for all time, it’s passed internal to different locales of the mind, So, (for example, the hippocampus and amygdala) for long haul stockpiling and recovery. As So, these messages travel through the mind, they also make pathways that fill in as the premise of memory.
Development.
Various pieces of the cerebrum move distinctive body parts. The left half of the mind controls the developments of the correct side of the body, and the correct side of the cerebrum controls the developments of the left half of the body. At the point when you press your vehicle’s quickening agent with your correct foot, for instance, it’s the left half of your mind that sends the message permitting you to do it.
Fundamental body capacities. An aspect of the fringe sensory system called the autonomic sensory system controls a significant number of the body measures you never need to consider, such as breathing, assimilation, perspiring, and shuddering. The autonomic sensory system has two sections: Some common facts about your brain, on the other hand, the thoughtful sensory system and the parasympathetic sensory system.
The thoughtful sensory system readies the body for abrupt pressure as if you witness a burglary. When something startling occurs and Some common facts about your brain are rare in this car, the thoughtful sensory system makes the heartbeat quicker so it sends blood rapidly to the distinctive body parts that may require it. It additionally causes the adrenal organs at the head of the kidneys to deliver adrenaline, a hormone
Thus, that encourages give additional capacity to the muscles for a fast escape.
The parasympathetic sensory system does the inverse: It readies the body for rest. It likewise enables the stomach related lot to move along so our bodies can productively take in supplements from the food we eat.
The Hindbrain – Some common facts about your brain
Light entering the eye shapes a topsy turvy picture on the retina. The retina changes the light into nerve signals for the mind. The mind at that point turns the picture straight up and mentions to you what you’re seeing.
Hearing. Each stable you hear is the aftereffect of sound waves entering your ears. However, causing your eardrums to vibrate. These vibrations at that point move along the little bones of the center ear and transform into nerve signals. The cortex at that point measures these signs, mentioning to you what you’re hearing.
Taste. The tongue contains little gatherings of tactile cells called taste buds that respond to synthetic substances in nourishments. So, Taste buds respond to sweet, harsh, pungent, unpleasant, and appetizing. The taste buds send messages to the territories in the cortex liable for handling taste.
Smell. Olfactory cells in the mucous layers coating every nostril respond to synthetics you take in
So, send messages along explicit nerves to the mind.
Contact. The skin contains a huge number of tactile receptors that assemble data identified with contact, weight, temperature, and torment and send it to the mind for handling and response.